AgentJet (AJet) is a cutting-edge, user-friendly agent tunning framework designed to optimize LLM models and agent workflows.
Simply provide your workflow (built from AgentScope, OpenAI SDK, Langchain, raw HTTP requests, or hybrid of all of them), training data, and reward function, and we will be ready to enhance your agents to their optimal performance!
Features
AgentJet aims to build a state-of-the-art agent tuning platform for both developers and researchers
- Easy and Friendly. AgentJet helps you tune models behind your agent workflows easily, optimizing your agents for top performance with minimal effort.
- Rich Tutorial Library. AgentJet provides a rich library of examples as tutorials.
- Efficient and Scalable. AgentJet uses [verl] as the default backbone (
--backbone=verl). However, we also support trinity as alternative backbone, accelerating your tuning process via fully asynchronous RFT. - Flexible and Fast. AgentJet supports multi-agent workflows and adopts a context merging technique, accelerating training by 1.5x to 10x when the workflow involves multi-turn (or multi-agent) conversations.
- Reliability and Reproducibility. Our team keeps track of framework performance across multiple tasks + major-git-version + training-backbones (under construction, still gathering data, comming soon).
For advanced researchers, AgentJet also provides high-resolution logging and debugging solutions:
- High-Resolution Logging: AgentJet allows users to save and inspect token-level rollout details, recording token IDs, token loss masks, and even token logprobs to facilitate workflow development and agent diagnostics.
- Fast Debugging: AgentJet also provides the
--backbone=debugoption for the best debugging experience, shortening your wait period from minutes to seconds after code changes and enabling breakpoint debugging in IDEs.
Quick Start
Installation
We recommend using uv for dependency management.
- Train the first agent
You can start training your first agent with a single command using a pre-configured YAML file:
Learn More
See the Math Agent example for detailed explanation.
Example Library
Explore our rich library of examples to kickstart your journey:
Math Agent
Training a math agent that can write Python code to solve mathematical problems.
AppWorld Agent
Creating an AppWorld agent using AgentScope and training it for real-world tasks.
Werewolves Game
Developing Werewolves RPG agents and training them for strategic gameplay.
Learning to Ask
Learning to ask questions like a doctor for medical consultation scenarios.
Countdown Game
Writing a countdown game using AgentScope and solving it with RL.
Frozen Lake
Solving a frozen lake walking puzzle using AgentJet's reinforcement learning.
Core Concepts
AgentJet makes agent fine-tuning straightforward by separating the developer interface from the internal execution logic.
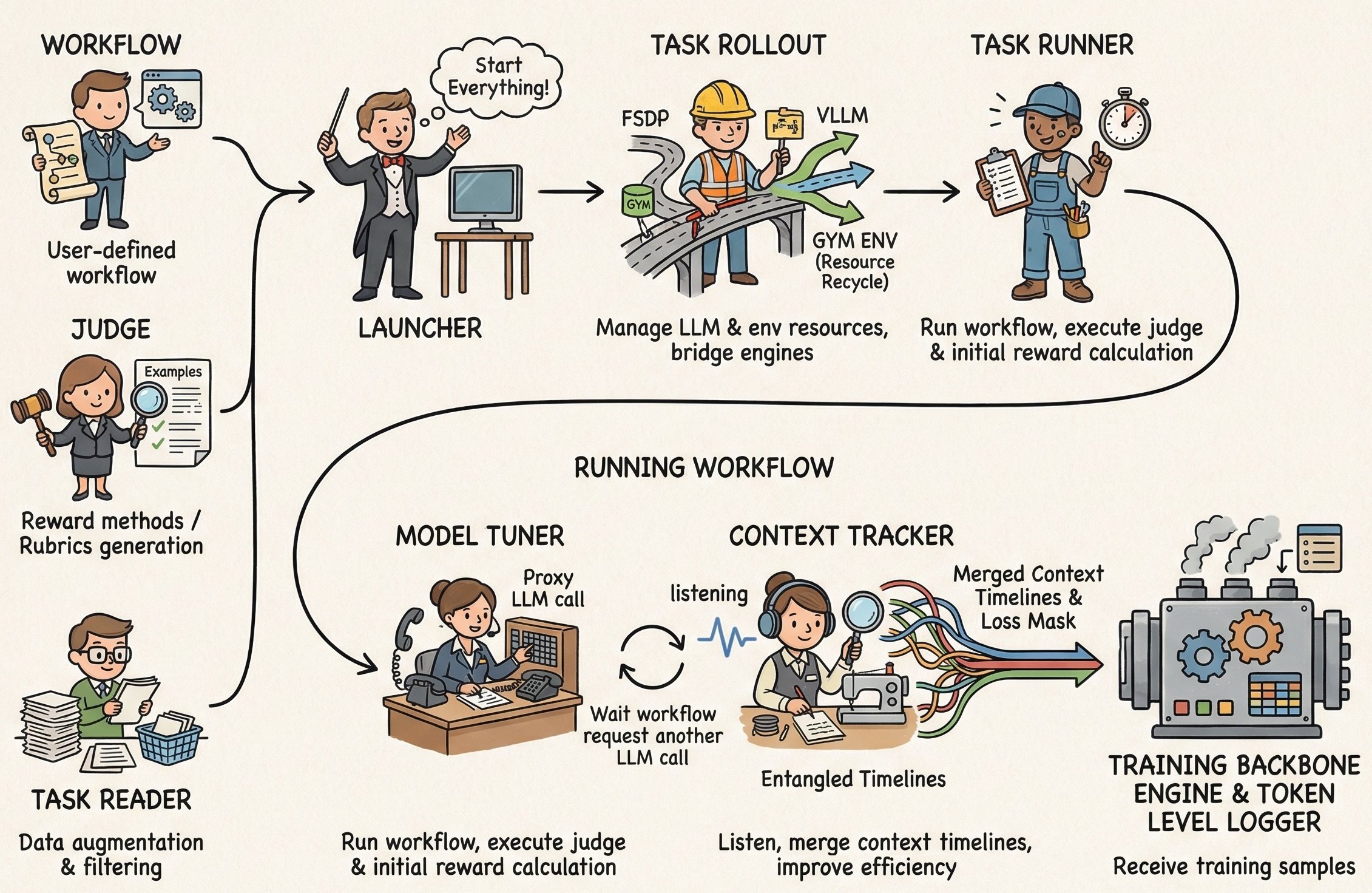
1. The User-Centric Interface
To optimize an agent, you provide three core inputs:
Trainable Workflow
Define your agent logic by inheriting the Workflow class, supporting both simple and multi-agent setups.
Task Reader
Load training tasks from JSONL files, HuggingFace datasets, or auto-generate from documents.
Task Judger
Evaluates agent outputs and assigns rewards to guide the training process.
2. Internal System Architecture
The internal system orchestrates several specialized modules to handle the complexities of RL training and agent interactions.
| Module | Description |
|---|---|
| Launcher | Manages background service processes (Ray, vLLM) and routes the backbone |
| Task Reader | Handles data ingestion, augmentation, and filtering |
| Task Rollout | Bridges LLM engines and manages the Gym environment lifecycle |
| Task Runner | Executes the AgentScope workflow and calculates rewards |
| Model Tuner | Forwards inference requests from the workflow to the LLM engine |
| Context Tracker | Monitors LLM calls and automatically merges shared-history timelines (1.5x-10x efficiency boost) |